Ever found yourself lost in a sea of information, desperately searching for a single, elusive fact? The answer, more often than not, lies within the humble index a meticulously crafted guide that unlocks the treasures hidden within vast archives of knowledge.
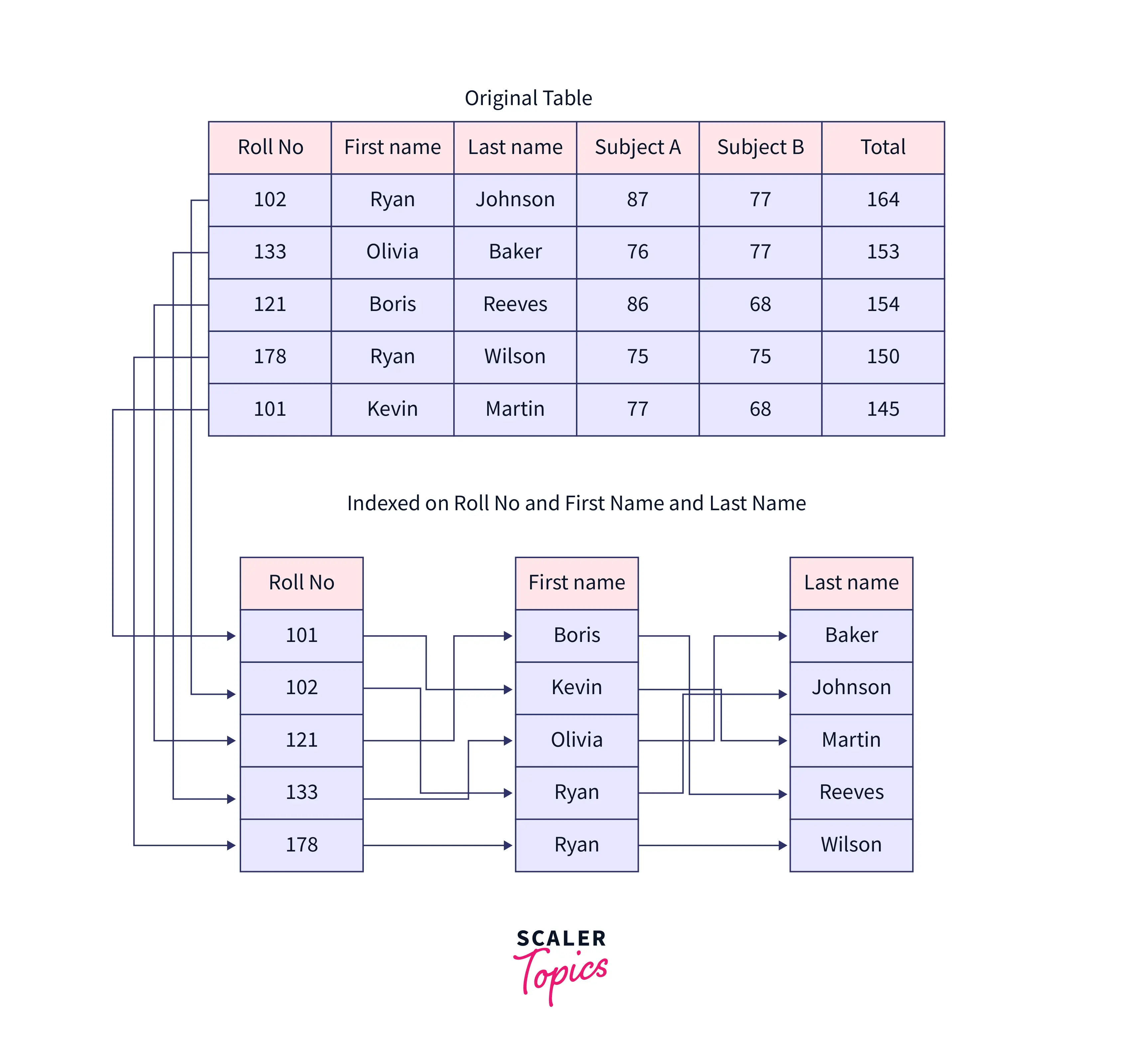
An index, at its core, is a systematic roadmap. Think of it as a highly organized table of contents, but instead of simply listing chapter headings, it delves into the minutiae of a work. Its a carefully compiled list of names, places, concepts, and keywords, meticulously arranged in alphabetical or numerical order, each entry meticulously linked to the exact location where that information can be found. This location is often a page number, but in the digital realm, it could be a hyperlink to a specific section of a website, a timestamp in a video, or a record within a sprawling database. Indexes are indispensable tools for researchers, scholars, and anyone who needs to quickly and efficiently pinpoint relevant information within a book, journal, database, or any other substantial resource. Consider the sheer volume of material published daily; without indexes, the task of research would be akin to finding a needle in a haystack. The index of a book, for instance, doesn't just tell you what the book is about in general terms; it tells you precisely where specific topics are discussed, allowing you to bypass irrelevant sections and focus on what matters most to your inquiry. The index of a journal, similarly, efficiently catalogs the articles within each issue, offering a bird's-eye view of the scholarly landscape.
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic listing or record of items, arranged alphabetically or numerically, providing quick access to specific information. |
| Purpose | To efficiently locate specific information within a larger body of work. |
| Examples | Book indexes, journal indexes, database indexes, search engine indexes, Consumer Price Index (CPI). |
| Arrangement | Typically alphabetical or numerical. |
| Benefits | Organization, access, retrieval, navigation, search, reference. |
| Website | American Library Association |
Beyond their role in traditional research, indexes play a crucial part in tracking trends and analyzing data over time. The Consumer Price Index (CPI), for example, is a prime illustration of this. The CPI meticulously tracks the average change in prices for a representative basket of goods and services purchased by consumers. By carefully monitoring the CPI, economists gain valuable insights into inflation, enabling them to make informed decisions about monetary and fiscal policy. Without such indexed data, it would be exceptionally difficult to accurately gauge the economic health of a nation and to respond effectively to fluctuating market conditions. The power of indexed data extends far beyond economics. In scientific research, for instance, indexed databases of research papers allow scientists to track the development of new technologies and identify emerging trends in their respective fields.
- Desi Mms Latest The Inside Scoop Youve Been Waiting For
- Noarmsgirl Leak The Untold Story Behind The Viral Sensation
The digital revolution has amplified the importance of indexes exponentially. In an era defined by information overload, the ability to sift through massive datasets quickly and efficiently is paramount. Search engines like Google rely heavily on sophisticated indexing algorithms to crawl the web and catalog billions of websites. These indexes act as the backbone of the internet, enabling users to find relevant content in a matter of seconds. Similarly, online databases like JSTOR, which house vast archives of academic journals, use indexes to help users locate specific articles based on keywords, authors, or publication dates. Without these indexes, navigating the digital landscape would be a chaotic and overwhelming experience. Imagine trying to find a specific piece of information on the internet without the assistance of a search engine a task that would be both time-consuming and, in many cases, impossible.
To reiterate, an index serves as a systematic listing or record of items, meticulously arranged, usually in alphabetical or numerical order, providing swift and efficient access to specific information residing within a larger body of work. These indexes are indispensable tools for anyone engaged in research or reference, as they empower users to rapidly and effortlessly locate relevant information within a wide array of resources, from books and journals to comprehensive databases.
- Organization: Indexes are instrumental in organizing information in a logical and consistent manner, streamlining the process of locating specific items. The methodical arrangement, whether alphabetical or numerical, provides a clear pathway through the material, making it easy to pinpoint the desired information.
- Access: Indexes provide rapid and effortless access to information, allowing users to locate specific items without the need to sift through entire documents. This saves valuable time and reduces the potential for frustration.
- Retrieval: Indexes are used to retrieve specific items from extensive collections, such as books, journals, and databases. They act as a targeted search mechanism, ensuring that the user can efficiently extract the precise information required.
- Navigation: Indexes can be used to navigate through vast bodies of information, such as websites and online databases. They offer a structured framework for exploring the content, allowing users to move seamlessly between different sections and topics.
- Search: Indexes are used to search for specific items within large collections, such as library catalogs and online databases. They provide a powerful search capability, enabling users to identify the relevant resources based on keywords or other criteria.
- Reference: Indexes are used to provide references to specific items, such as page numbers in a book or the titles of articles. This ensures that the user can easily verify the source of the information and trace it back to its original context.
The significance of these key aspects underscores the vital role indexes play as essential tools for research and reference. Indexes empower users to swiftly and effortlessly locate the information they require, resulting in significant time and effort savings. Furthermore, indexes are pivotal in organizing and managing information effectively, thereby facilitating the tracking of extensive datasets.
- Ramzi Alamuddin The Rising Star In Digital Marketing
- Hd Hub 4 U Com Your Ultimate Destination For Entertainment And More
Indexes stand as indispensable instruments for structuring information in a manner that facilitates the effortless retrieval of specific items. Without the guiding hand of an index, navigating a voluminous document or a collection of documents can prove a daunting task. Consider, for example, the challenge of locating a specific article within a journal devoid of an index. The arduous process would entail meticulously combing through each issue of the journal, one by one, until the desired article is finally unearthed. This could potentially consume a significant amount of time and engender considerable frustration.
Indexes offer a swift and uncomplicated means of identifying specific items within a comprehensive collection of documents. These indexes are typically organized in an alphabetical or numerical sequence, enabling users to promptly locate the item of interest. Furthermore, indexes can be harnessed to search for specific keywords or phrases, which proves invaluable when seeking information on a particular subject matter.
Indexes are an invaluable resource for researchers and anyone else who routinely engages with substantial collections of information. They streamline the process of information retrieval, saving both time and effort by providing a quick and efficient means of locating the required data.
The capacity to promptly and readily access information stands as a cornerstone of research and reference endeavors. Indexes furnish this access by meticulously organizing information in a logical and consistent fashion, simplifying the process of identifying specific items. In the absence of an index, the task of locating the necessary information, particularly within a voluminous document or a collection of documents, can become both arduous and time-intensive.
Consider, for instance, the scenario of attempting to locate a specific article within a journal lacking an index. The laborious process would involve meticulously examining each issue of the journal, one by one, until the desired article is eventually discovered. This could potentially consume a considerable amount of time and engender substantial frustration.
Indexes furnish a streamlined and uncomplicated means of identifying specific items within a comprehensive collection of documents. These indexes are typically arranged in an alphabetical or numerical order, enabling users to swiftly locate the item of interest. Furthermore, indexes can be employed to search for specific keywords or phrases, which proves invaluable when seeking information on a particular topic.
Indexes are an indispensable resource for researchers and anyone else who routinely engages with substantial collections of information. They streamline the process of information retrieval, saving both time and effort by providing a quick and efficient means of locating the required data.
In summary, the ability to access information quickly and easily is a key benefit conferred by indexes. Indexes facilitate this access by organizing information in a logical and consistent manner, simplifying the process of identifying specific items. This makes indexes an indispensable tool for research and reference purposes.
Indexes play a pivotal role in retrieving specific items from extensive collections, encompassing books, journals, and databases. Without the aid of an index, the task of locating a specific item can become both cumbersome and time-consuming. Envision, for instance, the challenge of locating a particular article within a journal lacking an index. The arduous process would necessitate meticulously examining each issue of the journal, one by one, until the sought-after article is eventually discovered.
Indexes provide a streamlined and efficient method for retrieving specific items from extensive collections. They are typically organized in an alphabetical or numerical order, enabling users to swiftly locate the item of interest. Additionally, indexes can be employed to search for specific keywords or phrases, which proves particularly beneficial when seeking information on a specific subject.
The ability to swiftly and effortlessly retrieve specific items from extensive collections constitutes a key advantage of indexes. Indexes empower users to locate the necessary information promptly and efficiently, resulting in both time and effort savings. Indexes serve as an indispensable tool for researchers and anyone else who routinely engages with substantial collections of information.
Indexes are indispensable for navigating through extensive bodies of information, such as websites and online databases. They offer a structured and organized approach to accessing the information you require quickly and easily.
- Organization: Indexes are commonly organized alphabetically or numerically, facilitating the effortless location of the information you seek. This proves particularly advantageous when working with a voluminous body of information, such as a website comprising hundreds or thousands of pages.
- Search: Indexes can also be utilized to search for specific keywords or phrases, which is helpful when seeking precise information on a particular topic.
- Hyperlinks: Indexes frequently incorporate hyperlinks to the complete text of the documents they reference, streamlining access to the necessary information without requiring manual searching.
- Context: Indexes can furnish context for the information they reference, aiding in the comprehension of a particular document or piece of information.
In general, indexes are essential tools for navigating through extensive bodies of information. They provide a structured and organized means of accessing the information you require promptly and effortlessly.
The capability to search for specific items within a larger collection stands as a significant advantage of indexes. Indexes provide this functionality by organizing information in a logical and consistent manner, thereby simplifying the identification of specific items. This proves particularly valuable when working with extensive collections of information, such as library catalogs or online databases.
For instance, envision the challenge of attempting to locate a particular book in a library lacking an index. The arduous process would necessitate searching through the entire library, one book at a time, until the sought-after book is eventually discovered. This could potentially consume a significant amount of time and engender considerable frustration.
Indexes facilitate the swift and effortless searching for specific items within larger collections. They are typically arranged in an alphabetical or numerical order, enabling users to quickly locate the item of interest. Furthermore, indexes can be employed to search for specific keywords or phrases, which proves particularly beneficial when seeking information on a particular subject.
The capability to search for specific items within a larger collection is essential for research and reference purposes. Indexes provide this functionality by organizing information in a logical and consistent manner, simplifying the identification of specific items. This renders indexes an indispensable tool for researchers and anyone else who routinely engages with extensive collections of information.
Indexes play a crucial role in providing references to specific items within a larger body of work. This is particularly important for research and reference purposes, as it allows users to quickly and easily locate the information they need. For example, the index of a book typically lists the page numbers where specific topics or keywords are discussed, while the index of a journal may list the titles and authors of articles published in that issue.
The ability to provide references to specific items is a key component of an index. Without references, it would be difficult for users to find the information they need quickly and easily. This is especially important for large bodies of work, such as books and journals, where it would be impractical to search through the entire document to find the information you need.
In addition to providing references to specific items, indexes can also provide additional information, such as context and background information. This can be helpful for users who are trying to understand the meaning of a particular document or piece of information.
Overall, the ability to provide references to specific items is a key benefit of indexes. This functionality makes it possible for users to quickly and easily find the information they need, which is essential for research and reference purposes.
Indexes are an essential tool for research and reference, as they provide quick and easy access to specific information within a larger body of work. However, there are some common misconceptions and questions about indexes that we will address in this FAQ section.
Question 1: What is the difference between an index and a table of contents?
An index is a detailed listing of specific items within a larger body of work, typically arranged in alphabetical or numerical order. A table of contents, on the other hand, is a general overview of the main sections or chapters of a book or document.
Question 2: How do I use an index?
To use an index, simply look up the topic or keyword you are interested in. The index will then provide you with a list of page numbers or other references where you can find more information on that topic.
Question 3: Are indexes only found in books?
No, indexes can be found in a variety of resources, including journals, databases, and websites. Indexes can also be found in digital and electronic formats.
Question 4: How do I create an index?
Creating an index can be a time-consuming task, but it is essential for ensuring that your document is easy to navigate and use. There are a number of software programs that can help you create an index, or you can create one manually.
Question 5: What are some of the benefits of using an index?
Indexes provide a number of benefits, including:
- Quick and easy access to specific information
- Improved navigation and usability of documents
- Increased efficiency and productivity
An index is a systematic listing or record of items, usually arranged in alphabetical or numerical order, that provides quick access to specific information within a larger body of work. Indexes are essential tools for research and reference, as they allow users to quickly and easily locate relevant information in books, journals, databases, and other resources.
In this article, we have explored the many benefits of using indexes, including their ability to organize information, provide access to specific items, and facilitate navigation through large bodies of information. We have also discussed the different types of indexes and how to create and use them effectively.
We encourage you to use indexes whenever you are working with large bodies of information. Indexes can save you time and effort by providing quick and easy access to the information you need.
- Vega Movies Your Ultimate Destination For Cinematic Adventures
- Michael Schoeffling The Rising Star Of The Entertainment Industry